Nitrogen Fixation Mechanism
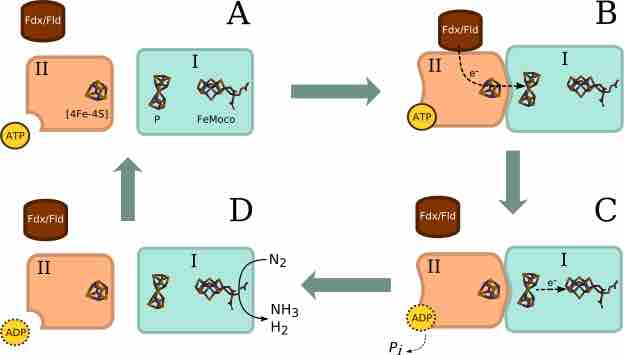
A General Catalytic Mechanism Scheme for Nitrogenase
A) Components I and II are dissociated; II is ready for reduction. B) ATP binds to component II, which receives electrons from an electron donor (ferredoxin or flavodoxin); binding of ATP induces an allosteric conformational change which allows association of the two proteins. Electrons flow from the [4Fe-4S] cluster on II to the P cluster on I. C) Electrons are further shuttled to the iron-molybdenum cofactor (FeMoco), and ATP is hydrolised to ADP. This step is repeated several times before a molecule of N2 can bind to FeMoco. D) The protein complex dissociates, and nitrogenase reduces dinitrogen to ammonia and dihydrogen. Legend:I: component I (dinitrogenase; MoFe protein); II: component II (dinitrogen reductase; Fe protein); ATP: adenosine triphosphate; ADP: adenosine diphosphate; Fdx: ferredoxin; Fld: flavodoxin.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: