Section 12
Biosynthesis
By Boundless
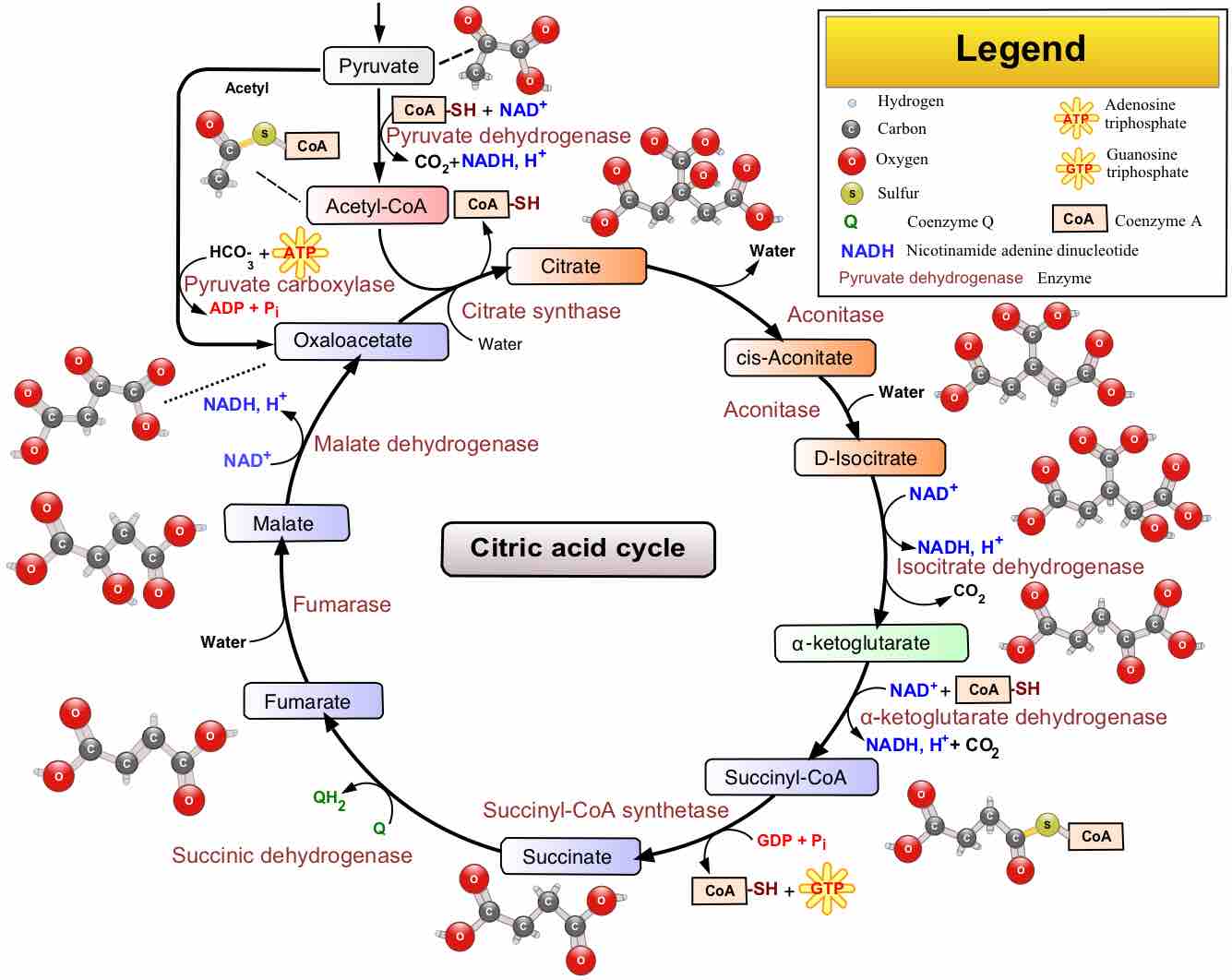
Major metabolic pathways require substrates to be acted upon for the formation of larger, more complex products.
Biosynthetic processes ensure the production of complex products necessary for cellular and metabolic processes.
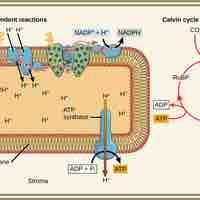
The Calvin cycle is organized into three basic stages: fixation, reduction, and regeneration.
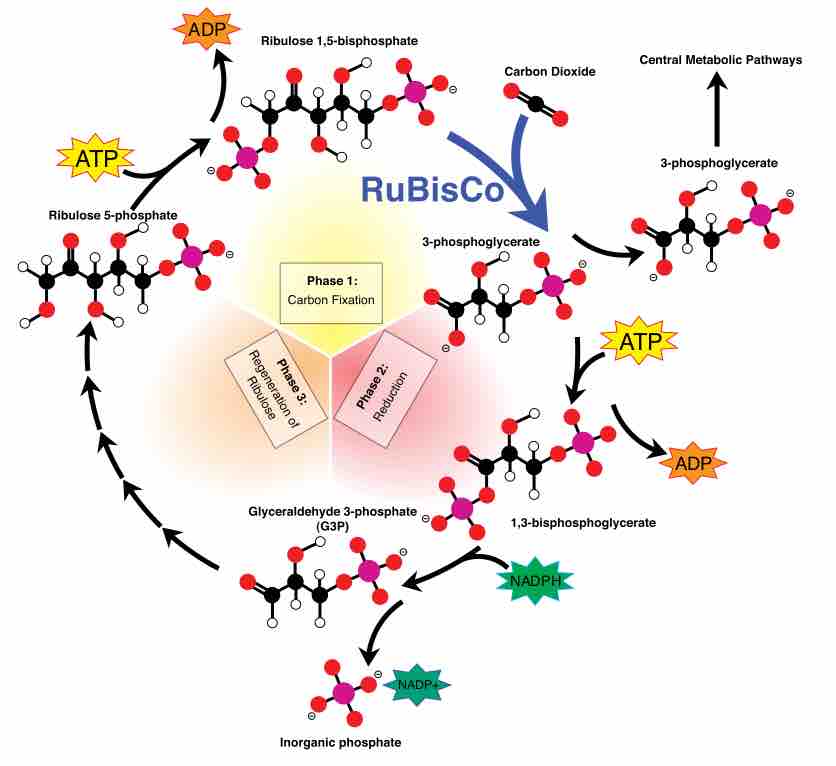
The Calvin Cycle involves the process of carbon fixation to produce organic compounds necessary for metabolic processes.
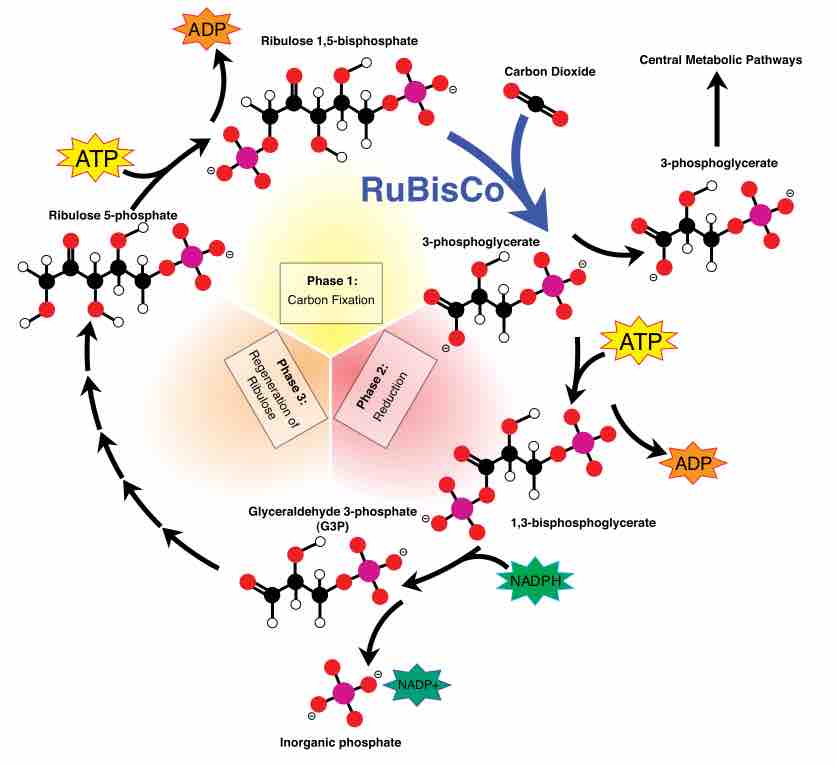
The Calvin cycle is a process that ensures carbon dioxide fixation in plants.
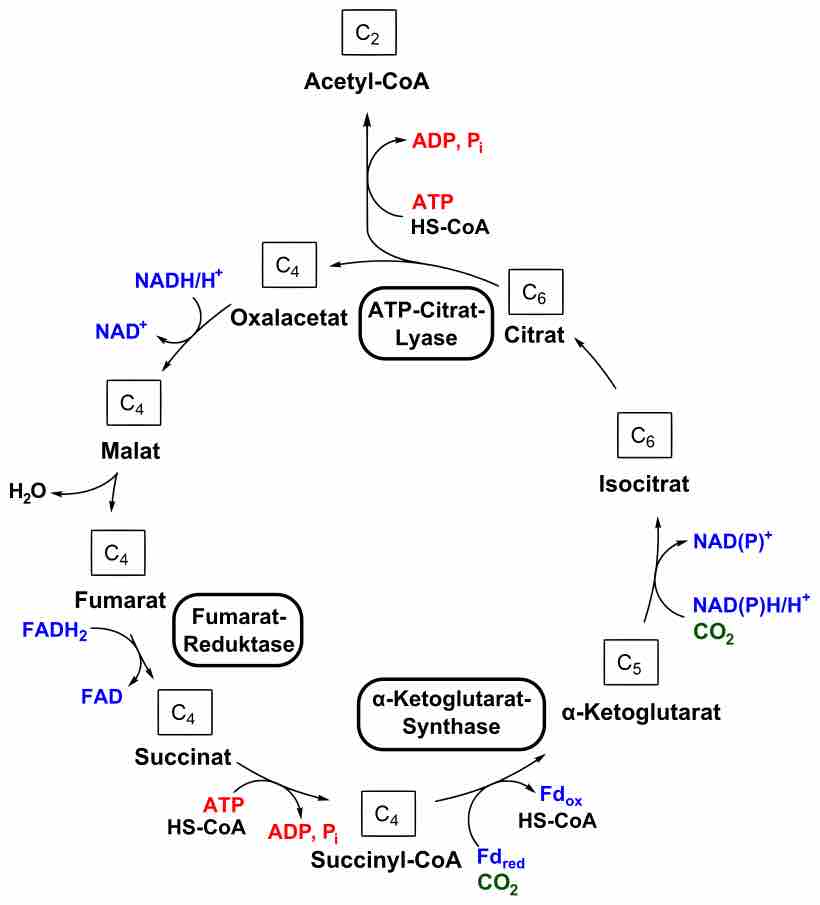
The reverse TCA cycle utilizes carbon dioxide and water to form carbon compounds.
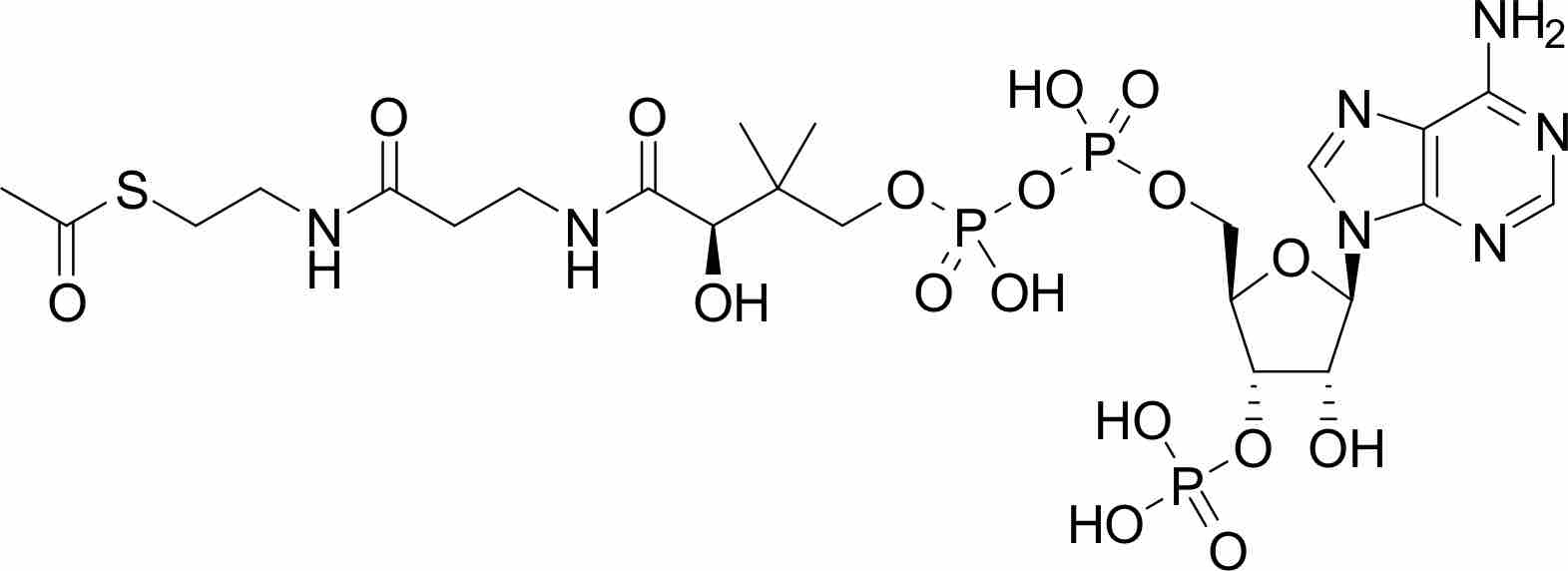
The acetyl-CoA pathway utilizes carbon dioxide as a carbon source and often times, hydrogen as an electron donor to produce acetyl-CoA.
The 3-hydroxypropionate cycle is a carbon fixation pathway that results in the production of acetyl-CoA and glyoxylate.