T lymphocytes have a dual specificity: they recognize polymorphic residues of self major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, which accounts for their MHC restriction; they also recognize residues of peptide antigens displayed by these MHC molecules, which is responsible for their specificity. MHC molecules and peptides form complexes on the surface of antigen presenting cells (APCs). The receptor that recognizes these peptide-MHC complexes is called the T Cell Receptor (TCR). Clones of T cells with different specificities express different TCRs.
The biochemical signals that are triggered in T cells following antigen recognition are transduced not by the TCR itself, but by invariant proteins (CD3, and zeta), which are non-covalently linked to the antigen receptor to form the TCR complex. T cells also express other membrane receptors that do not recognize antigens but participate in responses to antigens; these are collectively called 'accessory molecules'. The physiologic role of some accessory molecules is to deliver signals to the T cells that function in concert with signals from the TCR complex to fully activate the cell.
The antigen receptor of MHC-restricted CD4 helper T cells and CD8 cytolytic T cell is a heterodimer consisting of two transmembrane polypeptide chains, designated alpha and beta, covalently linked to each other by disulfide bonds. Each alpha and beta chain consists of one variable domain (V), one constant domain (C), a hydrophobic transmembrane region, and a short cytoplasmic region . The V regions of the TCR contain short stretches of amino acids where the variability between different TCRs is concentrated, and these form the hypervariable or complementarity-determining regions (CDRs). The recognition of peptide-MHC complexes is mediated by CDRs formed by both the alpha and beta chains of the TCR.
Prion-affected tissue
This micrograph of brain tissue reveals the cytoarchitectural histopathologic changes found in bovine spongiform encephalopathy. The presence of vacuoles, i.e. microscopic "holes" in the gray matter, gives the brain of BSE-affected cows a sponge-like appearance when tissue sections are examined in the lab.
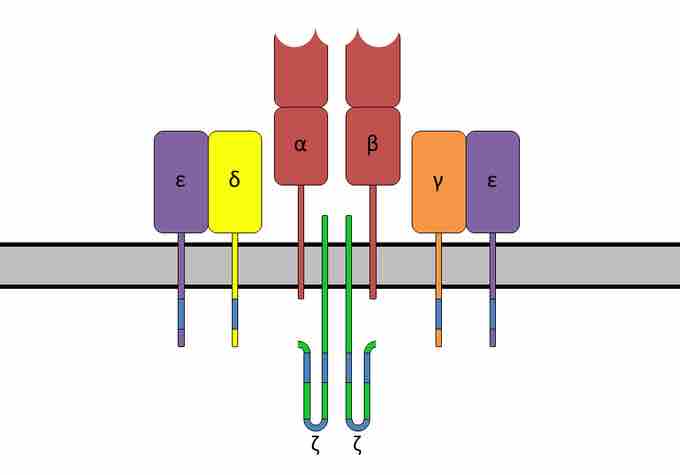
T cell receptor
T cell receptor consists of alpha and beta chains, a transmembrane domain, and a cytoplasmic region.