Although most of the information on a company's income tax return comes from the income statement, there often is a difference between pretax income and taxable income. These differences are due to the recording requirements of GAAP for financial accounting (usually following the matching principle and allowing for accruals of revenue and expenses) and the requirements of the IRS's tax regulations for tax accounting (which are more oriented to cash).
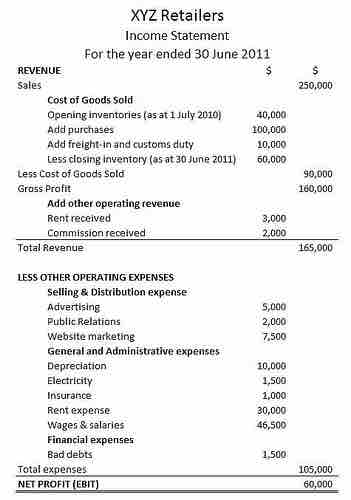
Income statement
GAAP and IRS accounting can differ.
Such timing differences between financial accounting and tax accounting create temporary differences. For example, rent or other revenue collected in advance, estimated expenses, and deferred tax liabilities and assets may create timing differences. Also, there are events, usually one time, which create "permanent differences," such as GAAP, which recognizes as an expense an item that the IRS will not allow to be deducted.
To achieve basic objectives and implement fundamental qualities, GAAP has four basic principles:
- The historical cost principle: It requires companies to account and report based on acquisition costs rather than fair market value for most assets and liabilities.
- The revenue recognition principle. It requires companies to record when revenue is (1) realized or realizable and (2) earned, not when cash is received.
- The matching principle. This governs the matching of expenses and revenues, where expenses are recognized, not when the work is performed or when a product is produced, but when the work or the product actually makes its contribution to revenue.
- The full disclosure principle. This suggests that the amount and kinds of information disclosed should be decided based on a trade-off analysis, since a larger amount of information costs more to prepare and use. GAAP reporting also suggests that income statements should present financial figures that are objective, material, consistent, and conservative.