A Boundless content module has a three-part structure: a learning objective, supporting text, and assessment items. The learning objective is the backbone of this structure: as a concrete statement of the expectation a student should be able to fulfill after studying the module, it gives the text a purpose and the assessment items something well-defined to assess.
Learning Objectives and Bloom's Taxonomy
Every Boundless learning objective is tagged with a Bloom's level, a number from 1 to 6 representing a tier of Bloom's Taxonomy. Bloom's Taxonomy is a hierarchy that describes levels of conceptual complexity. The six tiers correspond to the depth of conceptual thinking required to carry out the objective, with six requiring the deepest thought. The levels are as follows:
- Remembering
- Comprehending
- Applying
- Analyzing
- Evaluating
- Creating and Synthesizing
All Boundless learning objectives begin with a verb describing a concrete action, like "explain," "list," or "calculate." The learning objectives are tagged with a Bloom's level based on the first word of the learning objective.
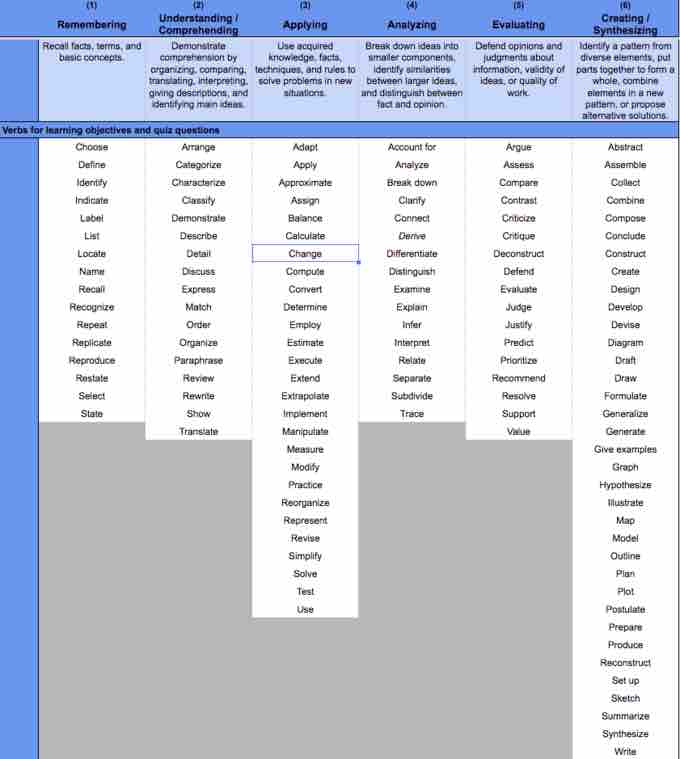
Boundless's Bloom's Taxonomy
Every Boundless learning objective begins with a verb from the Bloom's level appropriate to the concept it is a part of.
Limitations of Bloom's Taxonomy
Bloom's Taxonomy is an incredibly useful tool—it gives an idea, at a glance, of the relative conceptual depth of a learning objective.
That said, we also realize that the taxonomy is not ironclad. It is not a rigid scientific system of classification; in addition, not all possible learning objectives beginning with the verb "calculate" necessarily require the same level of conceptual thinking! We take care to write learning objectives that begin with a verb that reflects the depth of the content it is associated with.