Free Trade
Free trade is a policy where governments do not discriminate against exports and imports. There are few or no restrictions on trade and markets are open to both foreign and domestic supply and demand.
Advantages
Free trade is beneficial to society because it eliminates import and export tariffs. Restricted trade affects the welfare of society because although producers experience increases in surplus and additional revenue, the loss faced by consumers is greater than any benefit obtained . When a country trades freely with the rest of the world, it should theoretically produce a net gain for society and increases social welfare. Free trade policies consist of eliminating export tariffs, import quotas, and export quotas; all of which cause more losses than benefits for a country. With free trade in place, the producers of the exported good in exporting countries and the consumers in importing countries all benefit.
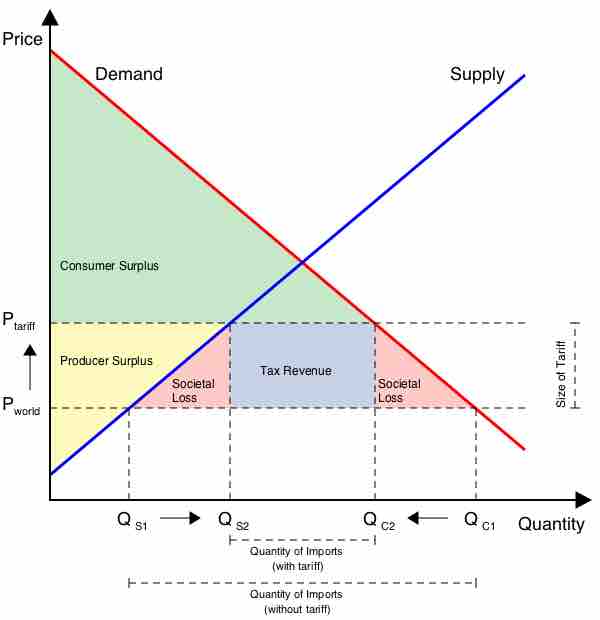
Tariffs
This image shows what happens to societal welfare when free trade is not enacted. Tariffs cause the consumer surplus (green area) to decrease, while the producer surplus (yellow area) and government tax revenue (blue area) increase. The amount of societal loss (pink area) is larger than any benefits experienced by the producers and government. Free trade does not have tariffs and results in net gain for society.
Disadvantages
One of the main disadvantages is the selective application of free trade. Economic inefficiency can be created through trade diversion. It is economically efficient for a good to be produced in the country with the lowest production costs. However, this does not always occur if a high cost producer has a free trade agreement and the low cost producer does not. When free trade is applied to only the high cost producer it can lead to trade diversion to not the most efficient producer, but the one facing the lowest trade barriers, and a net economic loss. Free trade is highly effective and provides society with a net gain, but only if it is applied.
Due to industry specializations, many workers are displaced and do not receive retraining or assistance finding jobs in other sectors. The nature of industries and trade increases economic inequality. As a result of unskilled workers the wages within the various industries may decline.
Another disadvantage is that by increasing returns to scale, can cause certain industries to settle in an geographically area where there is not comparative advantage. Despite this disadvantage, the level of output that is generated by free trade for both the "winner" and the "loser" is increased substantially.
The Results of Free Trade
Economists have studied free trade extensively and although it creates winners and losers, the main consensus is that free trade generates a large net gain for society. In a 2006 survey of American economists, it was found that 85.7% believed that the U.S. should eliminate any remaining tariffs and trade barriers. Economists professor N. Gregory Mankiw explained that, "few propositions command as much consensus among professional economists as that open world trade increases economic growth and raises living standards. "