Usually when economists use the term crowding out they are referring to the government using up financial and other resources that would otherwise be used by private enterprise. However, some commentators and other economists use crowding out to refer to government providing a service or good that would otherwise be a business opportunity for private industry.
The macroeconomic theory behind crowding out provides some useful intuition. What happens is that an increase in the demand for loanable funds by the government (e.g. due to a deficit) shifts the loanable funds demand curve rightwards and upwards, increasing the real interest rate. A higher real interest rate increases the opportunity cost of borrowing money, decreasing the amount of interest-sensitive expenditures such as investment and consumption. Thus, the government has crowded out investment .
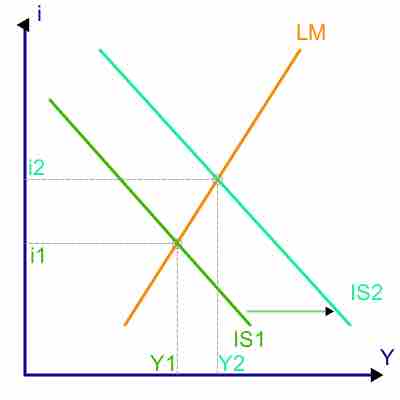
Crowding out Chart
When crowding-out occurs, the Investment-Savings (IS) curve moves to the right, causing higher interest rates (i) and expansion in the "real" economy (real GDP, or Y). LM stands for Liquidity Preference - Money Supply.
Borrowing and Crowding Out
In economics, crowding-out occurs when increased government borrowing reduces investment spending. The increased borrowing crowds out private investing.
If an increase in government spending and/or a decrease in tax revenues leads to a deficit that is financed by increased borrowing, then the borrowing can increase interest rates, leading to a reduction in private investment. There is some controversy in modern macroeconomics on the subject, as different schools of economic thought differ on how households and financial markets would react to more government borrowing under various circumstances.
Crowding-Out and Stimulus Programs
The extent to which crowding out occurs depends on the economic situation. If the economy is at capacity or full employment, then the government suddenly increasing its budget deficit (e.g., via stimulus programs) could create competition with the private sector for scarce funds available for investment, resulting in an increase in interest rates and reduced private investment or consumption. Therefore, the effect of the stimulus is offset by the effect of crowding out.