The long-run supply curve of a market is the sum of a series of short-run supply curves in the market (). Prior to determining how the long-run supply curve looks, its important to understand short-run supply curves.
Long-run Supply Curve
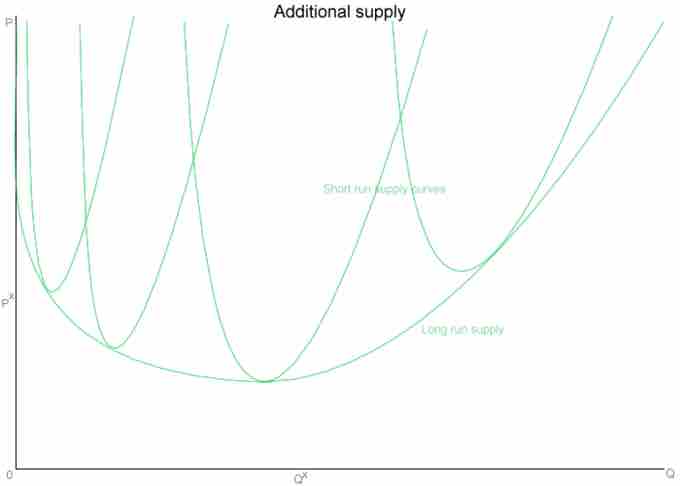
As the chart demonstrates, a market's long-run supply curve is the sum of a series of short-run supply curves in a given market.
Short-Run Supply Curves
While most people focus on the second half of a supply curve, which has a positive slope, that is not how the supply and pricing decision works in practice. As you can see from the chart, the first items that are produced start out with a very high price. This is because it is very expensive for a producer to manufacture one item. The producer has to incur fixed costs, such as learning the necessary skills to produce the item and purchasing new tools. These initial fixed costs make the cost of producing one good very expensive.
However, as more goods are produced, those initial fixed costs are spread out over more items. This decreases the price of per unit of each good produced for a period of time. As a result, in the early stages of production the supply curve is sloping downward as you can see in the chart. This period of supply is known as "increasing returns to scale," because a proportional increase in resources yields a greater proportional increase in output.
At some point, the per unit share of fixed costs becomes less than the variable costs of producing one more item. Variable expenses include purchasing more raw materials to manufacture another item. When this occurs, the supply curve slopes upward. Thus, in the short-run, a market's supply curve looks like an oddly shaped "u." This period of supply is known as "decreasing returns to scale," because a proportional increase in resources yields a smaller proportional increase in its amount in output. Between these two periods is the "constant returns to scale," where a proportion increase in resources yields an equal proportional increase in the amount of output.
Long-Run Supply Curves
A market's long-run supply curve is the sum of the market's short-run supply curves taken at different points of time. As a result, a long-run supply curve for a market will look very similar to short-run supply curves for a market, but more stretched out; the long-term market curve will a wider "u." A long-run supply curve connects the points of constant returns to scales of a markets' short-run supply curves. ; the bottom of each short-term supply curve's "u." Consider the attached chart.
The first short-run supply curve reflects what happens when a firm enters into a new market for the first time. When it does, it should make an economic profit. In a perfectly competitive market, firms can freely enter and exit an industry. When other business notice that the first firm is making it profit, they will enter the market to capture some of that profit and because there is nothing preventing them from doing so. In the early stages of the market, where only one or a few firms are producing goods, the market experiences increasing returns to scale, similar to what an individual firm would experience.
As more firms enter the market and time passes, production yields less and less returns in comparison to the production. Eventually the market reaches a state of constant returns to scale. How long this period of constant returns is varies by industry. Agriculture has a longer period of constant returns while technology has shorter.
Eventually, production of goods in a market yields less of a return than the amount of goods that go into product, which causes the market to enter into a period of decreasing returns to scale and the market's supply curve slopes upward.