Aggregate Supply
The aggregate supply is the relation between the price level and production of an economy. It is the total supply of goods and services that firms in a national economy plan on selling during a specific time period at a given price level.
Short-run Aggregate Supply
In the short-run, the aggregate supply curve is upward sloping because some nominal input prices are fixed and as the output rises, more production processes experience bottlenecks. At low levels of demand, production can be increased without diminishing returns and the average price level does not rise. However, when the demand is high, few production processes have unemployed fixed inputs. Any increase in demand and production increases the prices. In the short-run, the general price level, contractual wage rates, and expectations many not fully adjust to the state of the economy.
Shifts in the Short-run Aggregate Supply
The short-run aggregate supply shifts in relation to changes in price level and production. The equation used to determine the short-run aggregate supply is: Y = Y* + α(P-Pe). Y is the production of the economy, Y* is the natural level of production, coefficient α is always positive, P is the price level, and Pe is the expected price level.
In the short-run, examples of events that shift the aggregate supply curve to the right include a decrease in wages, an increase in physical capital stock, or advancement of technology. The short-run curve shifts to the right the price level decreases and the GDP increases. When the curve shifts to the left, the price level increases and the GDP decreases.
Any event that results in a change of production costs shifts the short-run supply curve outwards or inwards if the production costs are decreased or increased . Factors that impact and shift the short-run curve are taxes and subsides, price of labor (wages), and the price of raw materials. Changes in the quantity and quality of labor and capital also influence the short-run aggregate supply curve.
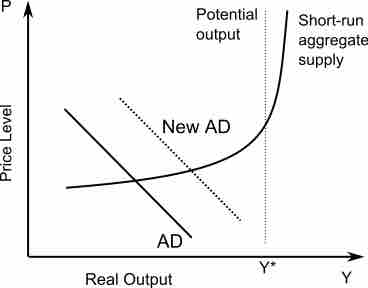
Short-run Aggregate Supply
This graph shows the Aggregate Suppy-Aggregate Demand model. In regards to aggregate supply, increases or decreases in the price level and output cause the aggregate supply curve to shift in the short-run.