Concept
Version 13
Created by Boundless
Hess's Law
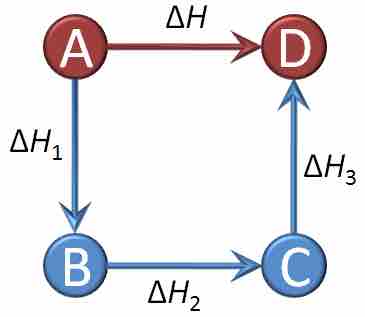
Graphical representation of Hess's law
The net reaction here is A being converted into D, and the change in enthalpy for that reaction is ΔH. However, we can see that the net reaction is a result of A being converted into B, which is then converted into C, which is finally converted into D. By Hess's law, the net change in enthalpy of the overall reaction is equal to the sum of the changes in enthalpy for each intermediate transformation: ΔH = ΔH1+ΔH2+ΔH3.
Source
Boundless vets and curates high-quality, openly licensed content from around the Internet. This particular resource used the following sources: