Three-Dimensional Lattice
The unique arrangement of atoms or molecules within a crystalline solid is referred to as the crystal structure of that material. A crystal structure reflects the periodic pattern of the atoms which compose a crystalline substance. Crystalline materials are so highly ordered that a crystal lattice arises from repetitions along all three spatial dimensions of the same pattern. The crystal lattice represents the three-dimensional structure of the crystal's atomic/molecular components.
The Unit Cell
The structure seen within the crystalline lattice of a material can be described in a number of ways. The most common way to describe a crystal structure is to refer to the size and shape of the material's characteristic unit cell, which is the simplest repeating unit within the crystal. In principle, one can reconstruct the structure of an entire crystal by repeating the unit cell so as to create a three-dimensional lattice.
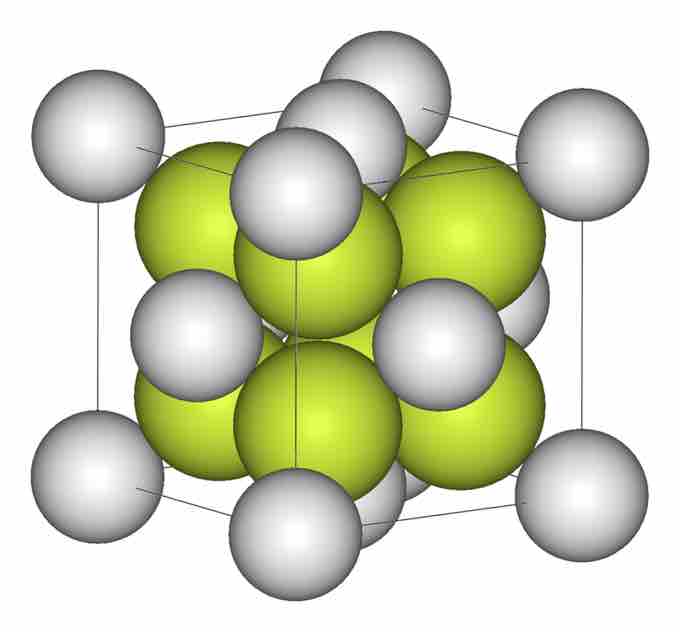
Unit Cell of Fluorite
This shows the simplest repeating unit within a crystal of the molecule fluorite, or calcium fluoride (CaF2). Notice that this unit cell contains several atoms. Calcium ions are depicted as gray spheres, and fluorine ions are yellow.
Packing of Atoms Within a Unit Cell
Within a crystalline material, each atom can be thought of as a sphere. These spheres are packed into unit cells. Each sphere that participates in a crystal structure has a coordination number, which corresponds to the number of spheres within the crystalline structure that touch the sphere that is being evaluated. For a sphere in the interior of a crystal lattice, the number of spheres contacting the sphere that is being evaluated is known as the bulk coordination number. For a sphere at the surface of a crystal, the number of spheres contacting the sphere being evaluated is known as the surface coordination number.
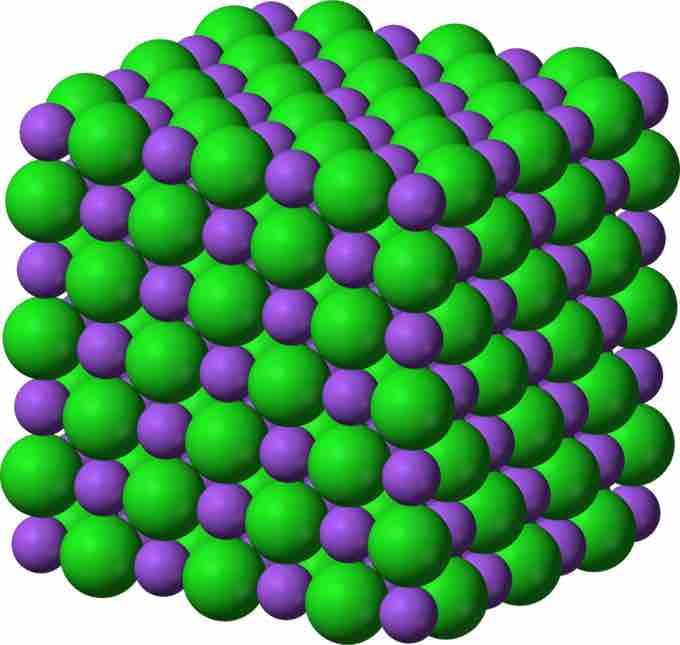
Crystalline Lattice
Sodium chloride crystal lattice
By considering how atomic spheres are arranged relative to one another, their coordination numbers, and the dimensions of the unit cell, it is possible to form a general view of the structure and complexity of particular crystal structures.