The Ideal Gas Equation in the form

Astronomical applications of the Ideal Gas Law
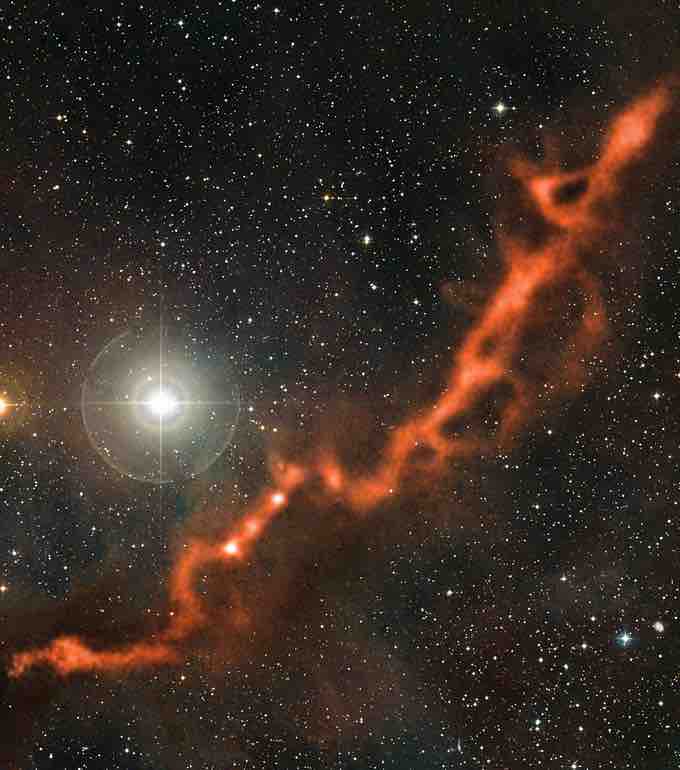
The Taurus Molecular Cloud consists of dust and various gases, including hydrogen and helium. The density form of the Ideal Gas Equation may be of theoretical use when studying such astronomical phenomena as star formation.
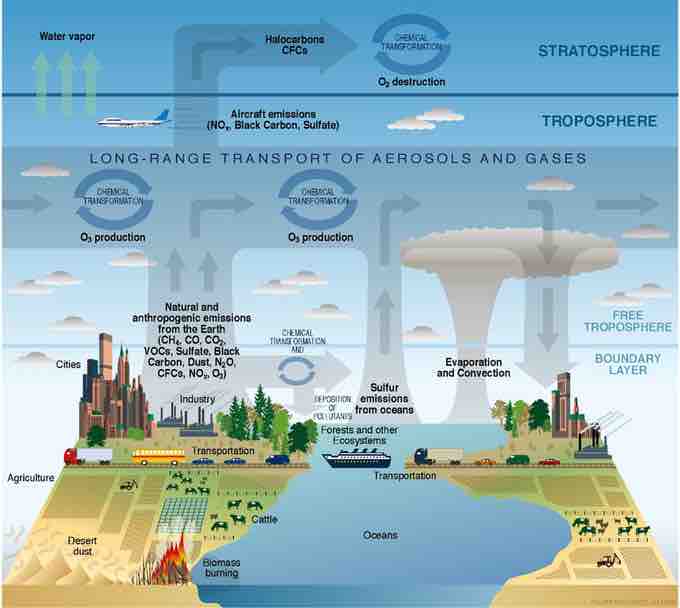
Atmosphere composition
Atmospheric science offers one plausible real-life application of the density form of the ideal gas equation. Earth's atmosphere is composed of gases that support life—as the image shows, oxygen involved in the water cycle, sulfur emissions from oceans, methane from agriculture, and more. The density form of the Ideal Gas Law enables us to study the behavior of these gases without enclosing them in a container of known volume.
Derivation of the Volume-Independent Ideal Gas Law
We know the Ideal Gas Equation in the form
If we substitute
Rearranging the above equation, we get:
Now, recall that density is equal to mass divided by volume:
The term
Rearranging in terms of D, we have:
This derivation of the Ideal Gas Equation allows us to characterize the relationship between the pressure, density, and temperature of the gas sample independent of the volume the gas occupies; it also allows us to determine the density of a gas sample given its pressure and temperature, or determine the molar mass of a gas sample given its density.