Definition of Avogadro's Law
Avogadro's Law (sometimes referred to as Avogadro's hypothesis or Avogadro's principle) is a gas law; it states that under the same pressure and temperature conditions, equal volumes of all gases contain the same number of molecules. The law is named after Amedeo Avogadro who, in 1811, hypothesized that two given samples of an ideal gas—of the same volume and at the same temperature and pressure—contain the same number of molecules; thus, the number of molecules or atoms in a specific volume of ideal gas is independent of their size or the molar mass of the gas. For example, 1.00 L of N2 gas and 1.00 L of Cl2 gas contain the same number of molecules at Standard Temperature and Pressure (STP).
Avogadro's Law is stated mathematically as:
V is the volume of the gas, n is the number of moles of the gas, and k is a proportionality constant.
As an example, equal volumes of molecular hydrogen and nitrogen contain the same number of molecules and observe ideal gas behavior when they are at the same temperature and pressure. In practice, real gases show small deviations from the ideal behavior and do not adhere to the law perfectly; the law is still a useful approximation for scientists, however.
Significance of Avogadro's Law
Discovering that the volume of a gas was directly proportional to the number of particles it contained was crucial in establishing the formulas for simple molecules at a time (around 1811) when the distinction between atoms and molecules was not clearly understood. In particular, the existence of diatomic molecules of elements such as H2, O2, and Cl2 was not recognized until the results of experiments involving gas volumes was interpreted.
Early chemists calculated the molecular weight of oxygen using the incorrect formula HO for water. This lead to the molecular weight of oxygen being miscalculated as 8, rather than 16. However, when chemists found that an assumed reaction of H + Cl
When chemists revisited their water experiment and their hypothesis that
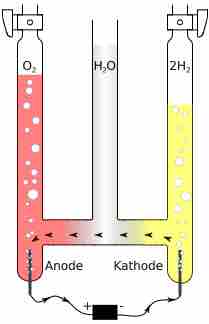
Experiment confirming the correct formula for water
It was originally assumed that 1 hydrogen and 1 oxygen atom went into a water molecule. Using Avogadro's Law, this experiment confirmed that 2 hydrogen and 1 oxygen form 1 water molecule.