The trigonometric functions (also called the circular functions) are functions of an angle. They are used to relate the angles of a triangle to the lengths of the sides of a triangle. Trigonometric functions are important in the study of triangles and modeling periodic phenomena, among many other applications.
The most familiar trigonometric functions are the sine, cosine, and tangent. In the context of the standard unit circle with radius 1, where a triangle is formed by a ray originating at the origin and making some angle with the
With this in mind, we can use the definition of a derivative to calculate the derivatives of different trigonometric functions:
For example, if
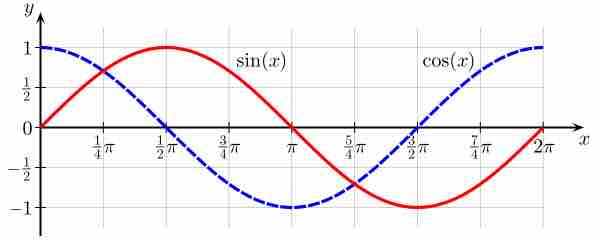
Sine and Cosine
In this image, one can see that where the line tangent to one curve has zero slope (the derivative of that curve is zero), the value of the other function is zero.
The same procedure can be applied to find other derivatives of trigonometric functions. The most common are the following: