In financial accounting, a liability is defined as an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future. A liability is defined by the following characteristics:
- Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time
- A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a specified or determinable date, on occurrence of a specified event, or on demand
- A duty or responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement
- A transaction or event obligating the entity that has already occurred
Liabilities in financial accounting need not be legally enforceable, but can be based on equitable obligations or constructive obligations. An equitable obligation is a duty based on ethical or moral considerations. A constructive obligation is an obligation that is implied by a set of circumstances in a particular situation, as opposed to a contractually based obligation. Examples of types of liabilities include money owing on a loan, money owing on a mortgage, or an IOU. Liabilities are debts and obligations of the business they represent that creditors claim on business assets. Liabilities are reported on a balance sheet and are usually divided into two categories:
- Current liabilities: these liabilities are reasonably expected to be liquidated within a year. They usually include payables such as wages, accounts, taxes, and accounts payables, unearned revenue when adjusting entries, portions of long-term bonds to be paid this year, short-term obligations (e.g., from purchase of equipment).
- Long-term liabilities: these liabilities are reasonably expected not to be liquidated within a year. They usually include issued long-term bonds, notes payables, long-term leases, pension obligations, and long-term product warranties.
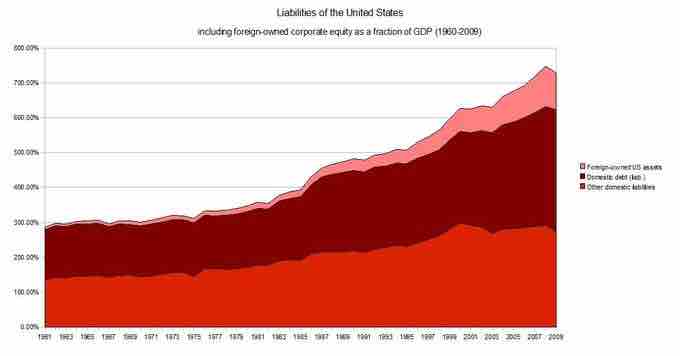
Liabilities of the United States
Liabilities of the United States as a fraction of GDP (1960-2009)