Section 4
Regulating Gene Expression in Cell Development
By Boundless
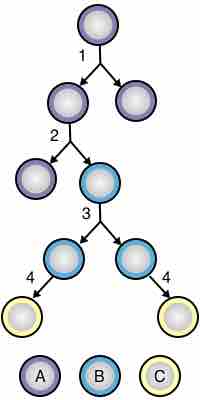
Symmetric division maintains stem cell lines and asymmetric division yields differentiated cells.
Cellular differentiation occurs so cells can specialize for different functions within an organism.
Cellular differentiation, a necessary process in development and maintenance of multicellularity, is regulated by transcription factors.
Animal bodies have three axes for symmetry (lateral-medial, dorsal-ventral and anterior-posterior) which are established in development.
During development it is critical that specific gene expression patterns are established to signal and differentiate the cells appropriately.
Cell migration is necessary for development and maintenance of multicellularity, and occurs through varying mechanisms.
Programmed cell death describes the death of a cell through a highly regulated process, and serves many functions in an organism.