In financial accounting, a liability is defined as an obligation of an entity arising from past transactions or events, the settlement of which may result in the transfer or use of assets, provision of services or other yielding of economic benefits in the future. A liability is defined by the following characteristics:
- Any type of borrowing from persons or banks for improving a business or personal income that is payable during short or long time;
- A duty or responsibility to others that entails settlement by future transfer or use of assets, provision of services, or other transaction yielding an economic benefit, at a specified or determinable date, on occurrence of a specified event, or on demand;
- A duty or responsibility that obligates the entity to another, leaving it little or no discretion to avoid settlement; and,
- A transaction or event obligating the entity that has already occurred.
The accounting equation relates assets, liabilities, and owner's equity: "" The accounting equation is the mathematical structure of the balance sheet.
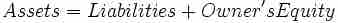
Accounting equation
Assets = Liabilities + Owner's Equity
In accounting and finance, equity is the residual claim or interest of the most junior class of investors in assets, after all liabilities are paid. If liability exceeds assets, negative equity exists. In an accounting context, shareholders' equity (or stockholders' equity, shareholders' funds, shareholders' capital, or similar terms) represents the remaining interest in assets of a company, spread among individual shareholders of common or preferred stock.
At the start of a business, owners put some funding into the business to finance operations. This creates a liability on the business in the shape of capital, as the business is a separate entity from its owners. Businesses can be considered, for accounting purposes, sums of liabilities and assets: this is the accounting equation. After liabilities have been accounted for, the positive remainder is deemed the owner's interest in the business.
In financial accounting, owner's equity consists of the net assets of an entity. Net assets is the difference between the total assets of the entity and all its liabilities. Equity appears on the balance sheet, one of the four primary financial statements.
The assets of an entity includes both tangible and intangible items, such as brand names and reputation or goodwill. The types of accounts and their description that comprise the owner's equity depend on the nature of the entity and may include: Common stock, preferred stock, capital surplus, retained earnings, treasury stock, stock options and reserve.
The total changes to equity is calculated as follows:
Equity (end of year balance) = Equity (beginning of year balance) +/- changes to common or preferred stock and capital surplus +/- net income/loss (net profit/loss earned during the period) − dividends. Dividends are typically cash distributions of earnings to stockholders on hand and they are recorded as a reduction to the retained earnings account reported in the equity section.