Activities of the business include operating activities, investing activities, and financing activities .
Business activities
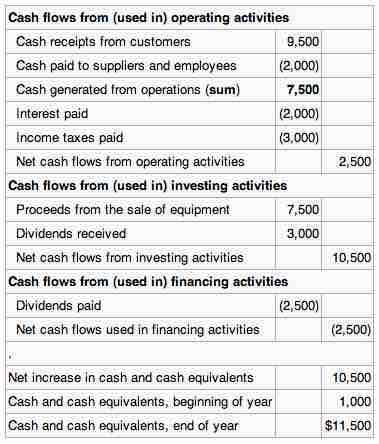
Business activities include operating, investing and financing activities.
Operating activities, or the fundamental activities the business engages in can include the production, sales, and delivery of the company's product as well as collecting payment from its customers. This could include purchasing raw materials, building inventory, advertising, and shipping the product. Under GAAP, operating cash flows include:
- Receipts from the sale of goods or services
- Receipts for the sale of loans
- Debt or equity instruments in a trading portfolio
- Interest received on loans
- Payments to suppliers for goods and services
- Payments to employees or on behalf of employees
- Interest payments (alternatively, this can be reported under financing activities in IAS 7 and US GAAP)
- Buying merchandise.
In addition to operating activities businesses engage in non-operating activities. Non-operating activities are not related to the day-to-day, ongoing operations of a business. Non-operating cash flows include borrowings, the issuance or purchase of stock, asset sales, dividend payments, and other investment activity.
Some examples of non-operating activities include:
Investing activities include purchases or sales of an asset (assets can be land, building, equipment, marketable securities, etc.), loans made to suppliers or received from customers, payments related to mergers and acquisitions, and dividends received.
Financing activities include the inflow of cash from investors such as banks and shareholders, as well as the outflow of cash to shareholders as dividends as the company generates income. Other activities which impact the long-term liabilities and equity of the company are also listed in the financing activities.
As with operating activities GAAP principles dictate how non-operating items are classified on the statement of cash flows.